Building confidence in traffic data: The development of Expansion Factors
Learn more about expansion factors with Altitude by Geotab and how they enable organizations to enhance their transportation networks.

In a funding landscape defined by oversubscribed programs like RAISE and INFRA, ‘black box’’ data no longer suffices. Federal reviewers and other stakeholders increasingly scrutinize the data integrity behind the proposal to understand how the metrics were derived and whether or not they are believable.
Strong plans offer clear answers to fundamental questions: What kinds of trucks are using this corridor? Why are they there? What’s driving congestion, safety issues or infrastructure strain? And what verifiable data proves it?
Many agencies don’t have that level of insight because standard tools only count vehicles, not their intent, and black box algorithms are difficult to understand. Altitude’s Vocation framework solves both of those problems.
Traditional counters can’t distinguish a local service van from a long-haul freight truck. They can’t show whether a peak-hour spike is caused by last-mile parcel vans, recurring regional delivery loops or interstate freight. Yet these distinctions directly affect project evaluation.
Altitude’s Vehicle Vocation model fills this gap by classifying vehicles into five categories that are aligned with industry terminology and regulations:
By using unsupervised machine learning to analyze behavior across five million vehicles, Altitude removes human bias and reveals the natural operational clusters of freight movement. This provides planners with mathematical ‘ground truth’ rather than arbitrary definitions.
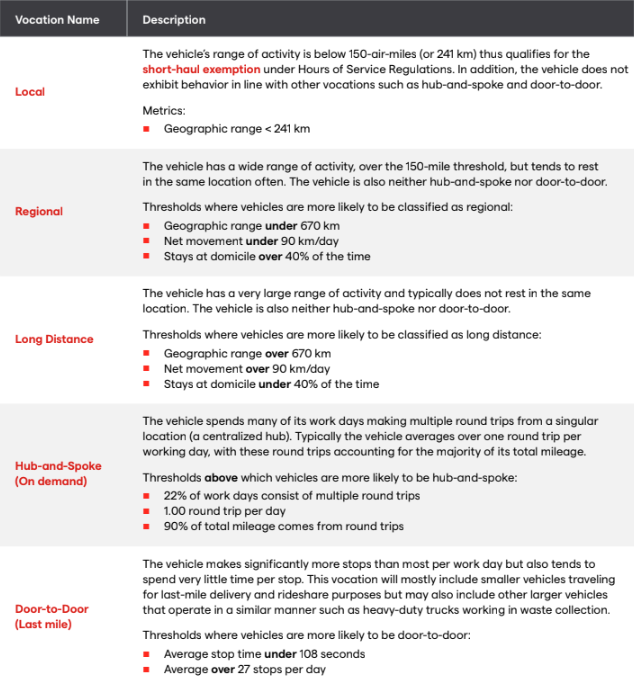
Figure 1: Altitude’s Vehicle Vocation classifications sort freight traffic into five funding-aligned categories.
With vocation intelligence, planners can finally explain why freight is moving the way it is, and where investment is needed to support economic growth.
Reviewers reward applications that present a clear problem and back it with auditable data. Vocation-based insight makes this possible through:
When reviewers see that actual vehicle behavior drives the analysis, a grant narrative becomes significantly more compelling. Especially when that data is clearly explainable to stakeholders in a town hall or federal review board. Altitude’s vocations are based on transparent behavioral thresholds (like range and stop frequency), not a black box.
Today’s funding environment pushes planners to defend their projects with a more nuanced understanding of freight movements. Vocation data helps agencies isolate and quantify the forces shaping corridor performance. For consultants, this means moving beyond generic heavy-vehicle counts to deliver precise corridor studies that differentiate the analysis.
Here are three high-impact use cases for strengthening applications:
Identify the true source of congestion or delay
Instead of saying “traffic is heavy,” planners can show whether the bottleneck is caused by:
Each scenario leads to a different, better-targeted solution and a stronger justification for investment.
Demonstrate economic activity linked to infrastructure needs
Vocation data reveals the freight purpose driving trips. Reviewers can better see whether the corridor supports:
This helps agencies tie project benefits to economic outcomes, which grant reviewers prioritize.
Build more precise cost-benefit analyses
When vocation is combined with weight class and industry, planners can quantify:
This granularity creates stronger cost-benefit ratios and clearer operational narratives.
Grant reviewers don’t just want to know that trucks use a specific corridor. They want to know which trucks are doing what and how often, and why it justifies investment.
As funding tightens, agencies with access to defensible, behavior-based freight data will outperform those relying on counts and assumptions. Altitude’s Vehicle Vocation classifications give planners the ability to quantify freight purpose with clarity and confidence.
Download the white paper to learn more about freight planning methodology with defensible, behavior-based vocation data that strengthens your grant narratives.
Learn more about expansion factors with Altitude by Geotab and how they enable organizations to enhance their transportation networks.
Our goal is simple: to provide you with the tools and insights you need to drive positive change in your organizations and communities.
Learn more about our expanded trip chaining options within the Geotab ITS Altitude platform which allows more custom analysis for users.